Lipoedema, a persistent and often misdiagnosed condition, affects millions of individuals worldwide, predominantly impacting women. Characterized by the disproportionate and abnormal accumulation of fat tissue, typically in the limbs, it can result in significant physical and emotional distress. While the exact cause remains elusive, recent research suggests a potential link between hormone imbalances and the onset of this condition.
Examining Lipoedema
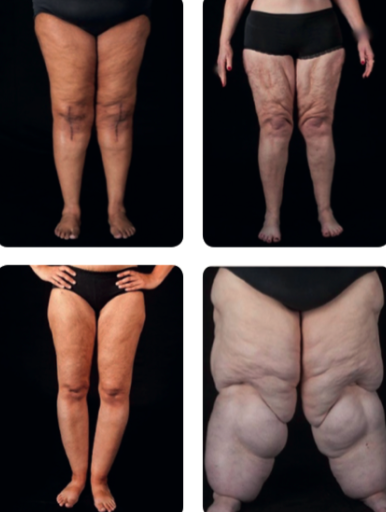
This is a progressive disorder characterized by:
- Symmetrical enlargement of subcutaneous fat tissue: Typically affecting the limbs, the disproportionate buildup of fat is noticeable compared to overall body size.
- Pain and tenderness: This is a hallmark symptom, often exacerbated by physical activity or hormonal changes.
- Easy bruising: Increased blood vessel fragility in affected areas leads to increased susceptibility to bruising.
- Abnormal texture: Uneven distribution of fat cells results in a bumpy or nodular appearance of the skin.
While it can affect individuals across various age groups, it predominantly manifests during periods of hormonal fluctuation, such as puberty, pregnancy, menopause, and with the use of hormonal contraceptives. This suggests a potential link between hormonal changes and the development and progression of the condition.
Unraveling the Hormonal Connection
Numerous hormones play a pivotal role in regulating fat metabolism and distribution in the body. These include:
- Estrogen: Essential for adipocyte (fat cell) proliferation and differentiation.** Studies suggest that an imbalance in estrogen levels, specifically an increased estrogen-to-progesterone ratio, may contribute to lipoedema.
- Progesterone: Balances estrogen effects and regulates fat storage.** A deficiency in progesterone may contribute to abnormal fat accumulation in individuals with lipoedema.
- Insulin: Regulates blood sugar levels and plays a role in fat storage.** Insulin resistance, often associated with obesity, can contribute to lipoedema development.
- Thyroid hormones: Regulate metabolism, indirectly influencing fat distribution.** While the precise mechanisms are still being investigated, research suggests a complex interplay between hormonal imbalances and genetic predisposition may be at play.
Lipoedema and Morbid Obesity: Understanding the Intersection
Morbid obesity, defined as a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than 40, poses a significant risk factor for lipoedema development. It’s crucial to note that not everyone with morbid obesity develops the condition, and there are individuals with lipoedema who do not have morbid obesity.
Both conditions present unique challenges for individuals and healthcare professionals. The increased fat tissue associated with morbid obesity can obscure lipoedema symptoms, complicating diagnosis. Furthermore, weight management strategies effective for general obesity may not be as beneficial for individuals with lipoedema.
Understanding the potential role of hormone imbalances in both conditions is essential for crafting effective treatment plans. Addressing underlying hormonal issues and implementing personalized weight management strategies can lead to substantial improvements in the physical and emotional well-being of individuals dealing with both morbid obesity and lipoedema.
Towards a Hopeful Future
While research on the connection between hormone disruption and lipoedema is ongoing, this knowledge holds great promise for the future. Understanding the hormonal factors at play could pave the way for:
- Enhanced diagnostic tools: Identifying hormonal imbalances may enable earlier and more accurate diagnosis of lipoedema.
- Personalized treatment plans: Tailoring strategies based on individual hormone profiles could enhance the management of the condition.
- Preventive measures: Identifying individuals at risk due to hormonal imbalances could facilitate early intervention and potentially prevent lipoedema development.
In conclusion, although the precise cause of lipoedema remains unclear, exploring the potential influence of hormone disruption marks a significant stride in understanding this intricate condition. Delving into the hormonal landscape and its impact on fat metabolism can pave the way for improved approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and management, offering a brighter future for individuals living with lipoedema.
Important Note:
This information serves for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Consult with your healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of lipoedema.
See also
Related Hormones
Understanding What Causes Short Height and.
Learn About Short Height: What Causes It, How to Diagnose It, and How to Treat It People who are short.
Read MoreSexual Disorders Comprehensive Treatments for all.
Sexual disorders: Understanding the Different Types, Causes, The diagnosis, and Successful Remedies Sexual disorders include a broad spectrum of disorders.
Read More