- January 16, 2025
- By drzaarofficial1@gmail.com
- 10
The Key Hormone for Digestive Health
Understanding Gastrin and Its Functions
Gastrin is a hormone primarily produced by the G-cells of the stomach lining. It plays a crucial role in the digestive process by stimulating the secretion of gastric acid (hydrochloric acid) in the stomach. Gastrin is released when food enters the stomach, particularly proteins, signaling the stomach to prepare for digestion. This hormone also promotes the growth of the stomach lining and enhances the motility of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrin’s effects are essential for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients properly, making it an integral part of the digestive system.
Key Functions of Gastrin
Gastrin is responsible for regulating the secretion of gastric acid, which is needed for the digestion of proteins and the absorption of various nutrients, including vitamins and minerals. By stimulating the parietal cells in the stomach lining to release hydrochloric acid, gastrin ensures that the stomach environment is acidic enough to break down food. Gastrin also promotes the growth and repair of the stomach lining, ensuring that it remains healthy and functional. Additionally, gastrin helps regulate the motility of the stomach and intestines, facilitating the smooth movement of food through the digestive tract.
The Role of Gastrin in Health and Disease
Gastrin is essential for optimal digestive function, and its imbalance can lead to digestive disorders. Overproduction of gastrin can result in excessive gastric acid secretion, contributing to conditions like peptic ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, a rare disorder where tumors cause an overproduction of gastrin. On the other hand, low gastrin levels can lead to inadequate acid production, which may impair digestion and nutrient absorption, contributing to conditions like hypochlorhydria (low stomach acid) or achlorhydria (absence of stomach acid). Disorders Linked to Gastrin Imbalance Excessive gastrin secretion is often linked to Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, where tumors in the pancreas or duodenum cause the overproduction of gastrin, leading to ulcers and digestive discomfort. High levels of gastrin can also contribute to GERD or other acid reflux disorders, leading to heartburn, regurgitation, and esophageal damage. Low gastrin levels, on the other hand, can impair digestion and absorption of nutrients, leading to conditions like bloating, indigestion, or vitamin deficiencies. Gastrin imbalances are typically diagnosed with blood tests and can be managed through medications that regulate stomach acid production.
Contact Us
+92-321-9700-700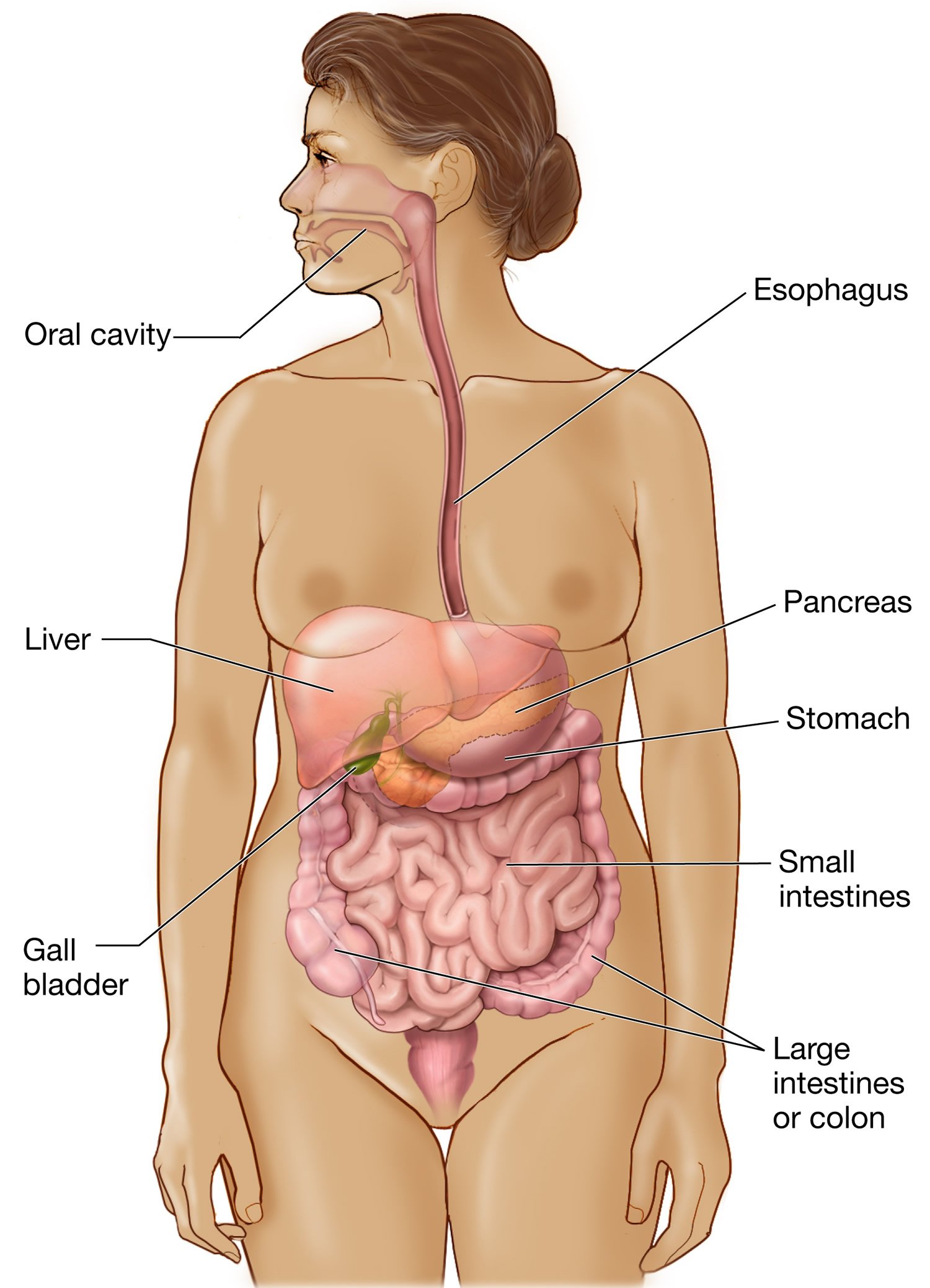
FAQs About Gastrin
1. What is gastrin?
Gastrin is a hormone produced by G-cells in the stomach that stimulates the secretion of gastric acid, essential for the digestion of food, particularly proteins.
2. How does gastrin regulate digestion?
Gastrin stimulates the parietal cells in the stomach lining to release hydrochloric acid, which creates an acidic environment necessary for breaking down proteins and absorbing nutrients.
3. What causes high gastrin levels?
High gastrin levels can be caused by tumors in the pancreas or duodenum (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome), chronic gastritis, or conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
4. What are the symptoms of high gastrin levels?
Symptoms of high gastrin levels include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, acid reflux, heartburn, and the formation of peptic ulcers.
5. How is gastrin tested?
Gastrin levels are typically measured through a blood test, which is used to diagnose conditions like Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, GERD, or gastric acid hypersecretion.
6. How does low gastrin affect digestion?
Low gastrin levels can lead to insufficient gastric acid production, impairing protein digestion and nutrient absorption. Symptoms include bloating, indigestion, and vitamin deficiencies.
7. Can gastrin levels be regulated?
Yes, gastrin levels can be regulated through medications that control stomach acid production, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers, as well as through lifestyle changes that reduce acid reflux.
8. How does gastrin influence the stomach lining?
Gastrin promotes the growth and repair of the stomach lining by stimulating the production of gastric mucosal cells, which help protect the stomach from the damaging effects of acid.
9. What is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome?
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is a rare disorder in which tumors in the pancreas or duodenum lead to excessive gastrin production, causing severe peptic ulcers, diarrhea, and acid reflux.
10. Can gastrin be used as a marker for digestive health?
Yes, gastrin levels can be measured to help diagnose digestive disorders, particularly those related to excessive gastric acid production or insufficient acid production.
